This guest article was written by Demetrios Zamboglou and Yiannis Menelaou of Lykke - a Swiss fintech company building a global marketplace on the Blockchain .
Global markets are undergoing a radical transformation, and the days of the IPO -- the Initial Public Offering -- are numbered. The expense, the barriers to entry, and the inefficiencies and inequities of traditional methods of raising capital are giving way to a whole new paradigm of openness and innovation, and it starts with something called an ITO.
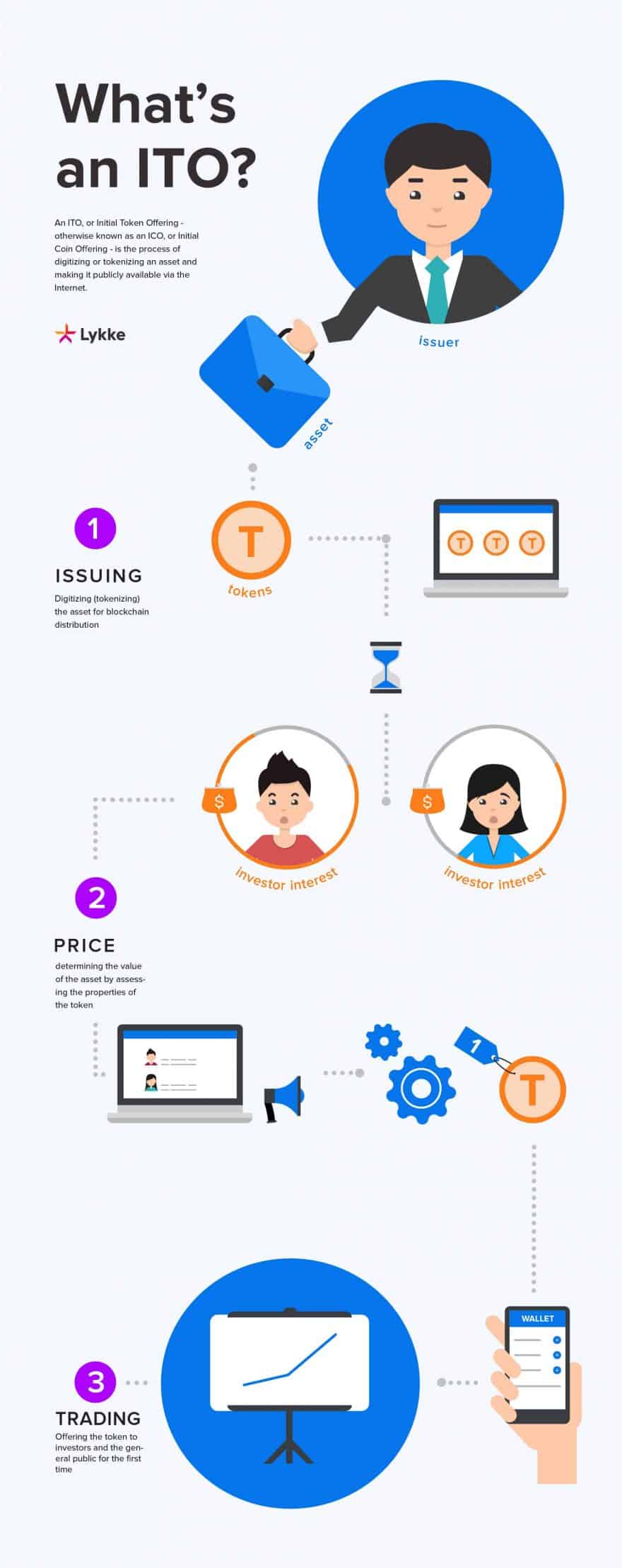
What’s an ITO?
An ITO, or Initial Token Offering -- otherwise known as an ICO, or Initial Coin Offering -- is the process of digitizing or tokenizing an asset and making it publicly available via the internet.
So you start with an asset, which can be absolutely anything of value, including a share of a project or company. By way of the ITO, you create digital tokens or coins to represent this asset, which you can then transfer electronically.
You can sell or exchange the tokens online in a process similar to crowdfunding. You can also list them on an online exchange, much in the same way that stocks appear on a stock market. The process resembles an IPO, but without the hefty costs involved or the limitations that routinely apply to equity-based assets.
In itself, the token represents a quantity of the physical asset or a portion of the underlying enterprise. This gives the issuer the flexibility to structure it as an item that has a face value but that can also act as an asset class in its own right, with its own associated privileges, such as voting rights, dividends, and capital appreciation. Then again, tokens can function as a medium of exchange, to redeem for goods and services directly from participating merchants.
One of the most attractive aspects of tokens to new investors is that their bearers can exchange them on the secondary market, directly with each other, without the need for a centralized agency to settle transactions.
It is worth mentioning that the process of exchanging traditional currencies for Cryptocurrencies is referred to as crypto-investing. Until recently, ITOs tended to focus on investments using crypto coins, such as bitcoin or ethers. But with tokens, investors can trade virtually anything, including crypto coins, but also anything else that can be quantified and digitized.
Who are the parties involved?
The ITO process usually involves two parties: the issuing body and the exchange.
The issuing body is the company conducting the ITO. This company is usually responsible for marketing the ITO and providing information about it to potential investors.
The exchange (or the crypto-exchange) is, in essence, the company that creates the environment for buyers and sellers to trade the token in the secondary market. In some situations, the exchange also provides two sub-functions:
- Acting as the underwriter, which is to assume responsibility for the whitepaper, or the official description of the technology and services on offer; and the terms and conditions, or the memorandum of operations
- Assuming responsibility for the technologies involved in the ITO process, such as client accounts and deposit addresses; payment systems; the trading GUI, or graphical user interface; the application program interface, or API; and the ability to cross list the token at various exchanges
How does the process work?
The company that wishes to have an ITO advertises the offering to prospective investors, much like a crowdfunded project. Investors express their interest in participating.
It is important to note that, for every ITO, there is a limited amount of time and a limited number of tokens. Therefore, the issuer is responsible for allocating the appropriate proportion of services or equity for each investment, all within the given time frame.
After this time has passed, the issuer publishes the results of the campaign and announces the exchange upon which the token will be traded. The exchange, in turn, prepares the token for listing.
The listing process requires that the token have a digital format that enables buyers and sellers to trade it much like they would purchase a share on an exchange. In the past, this token assumed the form of a colored coin, which is a fraction of a bitcoin that represents the value of the asset. Nowadays, there are additional methods, including Ethereum-denominated coins, otherwise known as ERC20 tokens. The ERC20 standard allows for programmable tokens that can execute functions and respond to events.
The exchange also determines the listing price and creates a market for the token. In some instances, the exchange acts as a market-maker by stabilizing price action and avoiding extreme price fluctuations and movements. In some cases, the free-floating rate can be based solely on the existing supply and demand provided by other market participants.
Price movements can be extremely volatile. Depending on market demand and supply, the token finds its ideal value where it stabilizes, similar to a publicly traded share.
Why are ITOs so popular?
An ITO is a progressive alternative to the traditional venture-capital method of seeking and acquiring funding. It discourages the tendency for a single investor to dominate the shareholder register and therefore influence company policy in a centralized way.
ITOs have become a global phenomenon, because they provide access to regions and investors from all around the world, in stark contrast to the smaller, more insular bands of traditional funding. Companies that take advantage of ITOs do not need to expend valuable resources competing for increasingly scarce venture capital. Instead, they can allocate more of their resources to serving their market, growing their team, and enhancing their product.
In a nutshell, ITOs:
- Provide access to global capital (funding, expansion, new markets, and so on)
- Utilize a cost-effective listing process, compared with cost-prohibitive IPOs
- Enable the market to assess new or disruptive technologies
- Promote diverse companies, products, and services
- Encourage innovation
- Open the market to incredible e-commerce opportunities