You have most likely heard words such as dApps and Web 3 being thrown around, especially if you are interested in cryptocurrency. Decentralized Applications can act as the Web 3’s App Store, allowing anything to be built purely on smart contracts, giving the user a trustless and permissionless experience.
What Is a dApp?
Decentralized Applications or dApps are run through a series of smart contracts which can operate by themselves on top of a blockchain, such as Ethereum or a peer-to-peer network.
Decentralized Applications mean there is no centralized authority that users need to trust, they are simply relying on the smart contracts to work properly.
They are utilized for many different sectors, most notably finance, and other more niche uses such as gaming and browsing with the use of Brave. Due to their decentralized nature, they are free from strict control over a singular governing body, allowing ambitious projects, un-restricted by conventional applications, to be built.
dApps are simply applications where people can interact with each other without a third party.
How Can I Interact with dApps?
Although Polygon is catching up, the majority of dApps are currently run on the Ethereum blockchain, being the second-biggest cryptocurrency by market capitalization.
There are several methods for accessing dApps, with one of the most common methods being via the MetaMask wallet. Utilizing the web3.js, Ethereums web API, MetaMask's first version of accessibility to dApps was presented in July 2016.
MetaMask is simply a browser extension self-custodial cryptocurrency wallet available on major browsers, such as chrome and firefox, enabling the user to connect their funds to dApps.
Many other wallets allow easy access to dApps such as:
- Coinbase wallet
- Trust Wallet
- Uniswap
Finding and Using dApps
dApps are most commonly accessed via a phone, however, there are a few solutions for using dApps on a desktop, such as the Coinbase wallet, dappradar.com or dapp.com where over 3,000 dApps can be explored.
It’s important to note, that you may have even used a dApp unknowingly, as they work similarly to traditional websites. What distinguishes dApps from regular websites are:
- Cryptocurrency wallet integration
- Read or write data to a blockchain
Endaoment, a public charity accepting crypto donations, allows wallet connections and is completely transparent through the blockchain. Their dApp is launched through their Web 2 website.
The Most Popular dApps
Depending on the metric you are using to gauge popularity, some of the biggest dApps are Decentralized Exchanges (DEX), such as Uniswap and Pancakeswap. However, other large dApps such as Splinterlands and Crazy Defense Heroes have large 30-day users, Splinterlands reaching over 500,000.
You can find a great list of dApps sorted by different metrics here.
Other large dApps in the financial world like MakerDAO are popularizing Decentralized stablecoins, such as their $DAI, which will help users navigate the complicated and volatile world of Decentralized Finance with limited risk.
Advantages of using dApps
Open Source
All dApps are completely open-source, meaning a user can manually check the code of the smart contract they will be interacting with, often using GitHub, to check for malicious lines of code and to ensure the app will work as suggested.
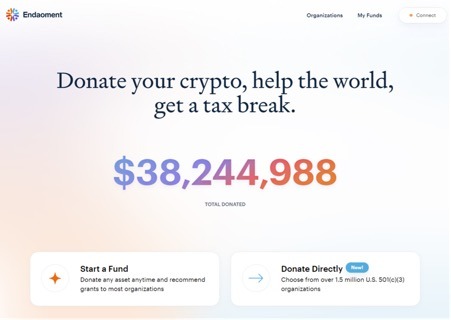
Here you can see Uniswaps GitHub, with all their smart contacts which make one of the largest DEXs in the world work. It would be hard to imagine a centralized bank offering similar transparency.
Trustless and Permissionless
To interact with dApps, or deploy your own smart contract, no real-world identification is needed. The biggest benefit of having trustless and permissionless applications is for finance. Decentralized exchanges such as Uniswap allow for a simple anonymous crypto wallet to be connected, with no further identification.
This inhibits any centralized authority from unfairly restricting or censoring a person's ability to have control over their finances and allows for the anonymity of financial transactions. Conversely, although the wallet address is anonymous, dApps deployed on blockchains will store all information forever on that specified blockchain, making it completely transparent and indisputable.
Trustless dApps routes us back to not having to trust a central authority that the app will work, you are trusting a smart contract.
Inability to Censor
Building on the last point, there is no central authority to restrict the usage or deployment of dApps by any one user, essentially promoting freedom of speech, movement and the right to financial independence.
No Single Points of Failure
Also, as dApps utilize smart contracts to run, once the smart contract is deployed there will be zero downtime for users, unlike traditional apps which are often a target of DoS attacks (Denial of Service).
Disadvantages of using dApps
Scalability
dApps built on blockchains are totally reliant on the blockchain's abilities regarding transaction speed and scalability. Ethereum, for example, is limited from 10 to 15 transactions per second, which often leads to network congestion that can slow dApps such as decentralized exchanges down.
Blockchains are required to validate every single transaction happening which takes resources, especially with Ethereum still utilizing a Proof of Work consensus mechanism, of which most dApps are built on top.
Going Mainstream
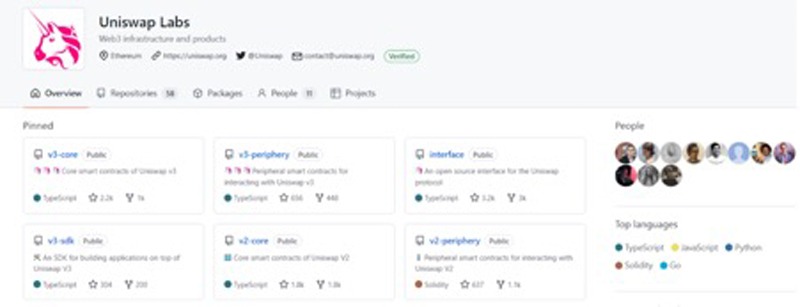
Most dApp users are seen as visionaries in the adoption cycle. Many blockades stopping dApps from going mainstream such as scalability and a much easier user interface (UI) must be removed before dApps and Web 3.0 can cross the chasm.
The chasm represents the toughest leap a product or technology must make to go from obscure to the mainstream market, and is required for true mass adoption.
Return to Centralization
Centralization is often ingrained into the human mind, with dApp developers helping one another build their apps, creating a service that mimics a centralized service with a lot more hassle. An example of this would be a dApp storing information server-side instead of by the user, such as keys to a cryptocurrency wallet.
Maintaining the Code
Fixing bugs or upgrading the contracts has often been cited by Ethereum developers as extremely difficult but necessary.
Education
Lastly, Decentralized Applications are simply harder to use and pose more risk to users than regular applications. For example, Decentralized Finance grants participants complete ownership of their digital assets, which comes with the complete reliability of their assets. If they lose the keys to their cryptocurrency wallet or make a mistake, the funds will be gone forever.
If someone were to lose a password on a centralized banking system, 24/7 hotlines are available to recover the funds.
This barrier of education may be the true battle for dApps to overcome.
Important Differences between Regular Apps and dApps
- Users of dApps are trusting the smart contracts, whereas regular app users trust the centralized authority.
- There is no central control on dApps, regular apps always have a center of command, which means they are more vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
- Users can access dApps with no personal information and without any tracking.
Why Bother with dApps?
Crypto optimists believe there will soon be a decentralized version of our traditional apps which we currently know and love, such as Peepeth, an alternative to Twitter. The hope is for dApps to slowly take back control over the internet, which big tech giants have monopolized and monetized under our feet, their ‘free’ products, that we drip-feed our actions into providing a lucrative behavioral surplus to be sold against our will, for the benefit of fake personalization.
Many may believe that to be a dramatization of the current state of the internet, although too often it has come true. Big tech giants, such as Facebook and Google, run the internet, which is where dApps step in to take back that control. The control is for no singular centralized authority, but for the user(s), built on open-source smart contracts that anyone can clearly see.
The best advice would be to try them for yourselves, educate yourself on the current state of the internet and take action which suits your wants and needs. Not all dApps will be a success and the best dApps that will exist currently do not, which makes the space even more exciting.
Are dApps the Future?
Many view Decentralized Applications as the Web 3 version of the App Store, a partnership that will be crucial to the widespread adoption of both Web 3 and dApps. There are still many boundaries to overcome, such as widespread utility and the removal of unnecessary friction. With more and more blockchains growing a larger base of dApps, such as Polygon, more developers will flock to the lucrative space and exponential growth will continue to take place.
Skeptics often rebuttal the mass adoption of Web 3 and dApps as ’building Decentralized Applications on centralized infrastructure does not make it decentralized’, which is the main argument for many against the current change. Centralized web services such as AWS (Amazon Web Service) are being used to host decentralized applications, defeating the often-cited goal of ‘removing big-tech's monopoly over technology.
If the Web 3 community can outgrow simply by providing Decentralized Finance and a few popular play-to-earn games, dApps may become the future of how we browse and ultimately use the internet.