Post-COVID, businesses, and consumers have increasingly relied on electronic transactions, a convenience that comes at a cost related to payment fees. Though these fees appear nominal on the surface, they can cumulatively erode profit margins, especially for growing businesses.
A recent study found that credit card processing fees alone cost US merchants around $100 billion in 2023. This figure underscores the necessity of recognizing and understanding the composition of payment fees. It might as well be the first step toward optimizing your financial strategy for business growth.
This blog, penned with two decades of expertise in payment processing, aims to decode the complex language of payment fees, offering tangible strategies and insights to help you increase the profit margins of your businesses.
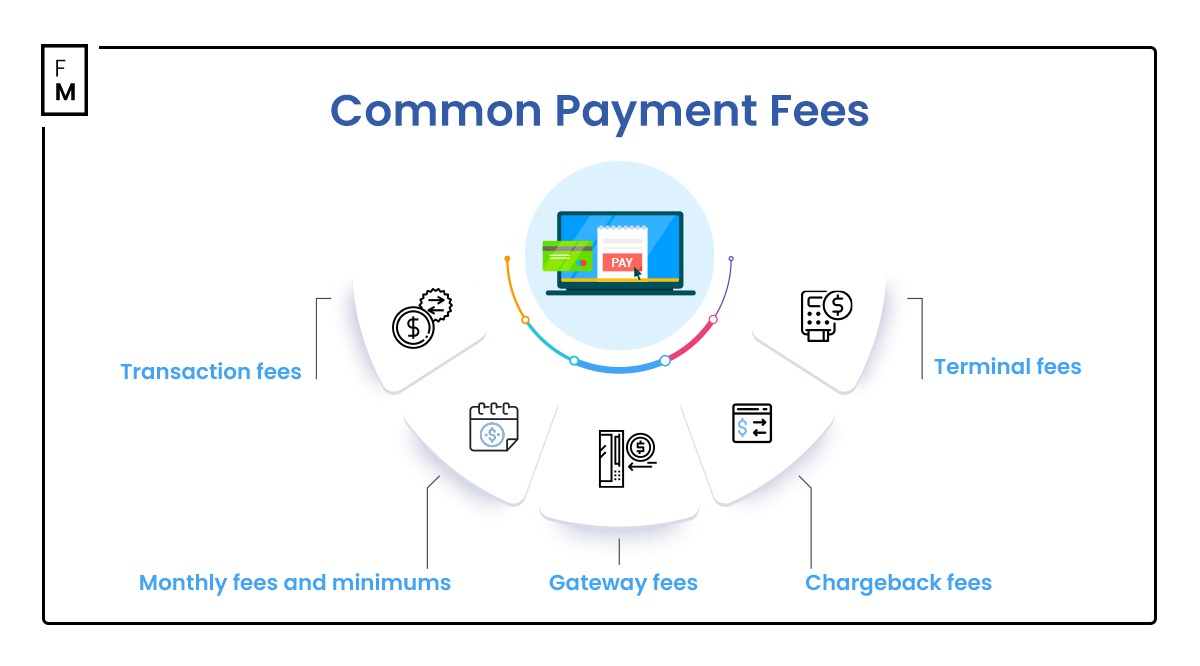
Common Payment Fees
As a business owner, understanding the different types of fees involved in payment processing can help you optimize your overall expenses and improve your profit margins. Some of these payment fees include:
- Transaction fees: One of the most common and perhaps the most straightforward fees, the transaction fee, is a percentage taken from each sale or transaction processed, plus a fixed fee. While these percentages may seem small, they can accumulate over time, impacting the overall profitability. Hence, you should always assess transaction fees in relation to your sales volume to accurately determine their impact.
- Monthly fees and minimums: Some payment processors may levy monthly fees for using their services. In particular, they have monthly minimums that mandate businesses to process a specified transaction volume or face additional charges. This is why you should select a payment processor whose fee structure aligns with your transaction volume, thereby helping you avoid unnecessary fees.
- Gateway Fees: Gateway fees apply to businesses using online transactions. Such fees are charged for using the electronic gateway that sends transaction data from the merchant to the processor. Because seamless online transactions are vital for modern businesses, you should look for integrated payment solutions that will minimize the extra cost.
- Chargeback fees: When we make online transactions, there are instances where they may fail. In the event that transactions are disputed, chargeback fees are incurred. These situations, while less frequent, can be costly.
- Terminal fees: For brick-and-mortar businesses, terminal fees apply to the physical devices used to process payments . You can justify the cost by investing in efficient and reliable payment terminals that enhance transaction speed and reliability.
Real-World Implications of Payment Fees on Operational Costs
The impact of payment fees on business operational costs is much more substantial than one might initially predict. At first glance, transaction fees of 2-3% of each sale may not raise concerns. However, these seemingly negligible percentages can have significant implications when applied to higher sales volumes.
Consider a business with an annual revenue of $1 million. In this scenario, transaction fees alone could translate to an annual expenditure of $20,000 to $30,000. This figure, while substantial on its own, represents only a fraction of the wider payment fee structure. Keep in mind that this does not account for additional monthly or annual service costs, terminal fees, setup fees, or incidental expenses like the chargeback and gateway fees, which can further inflate costs.
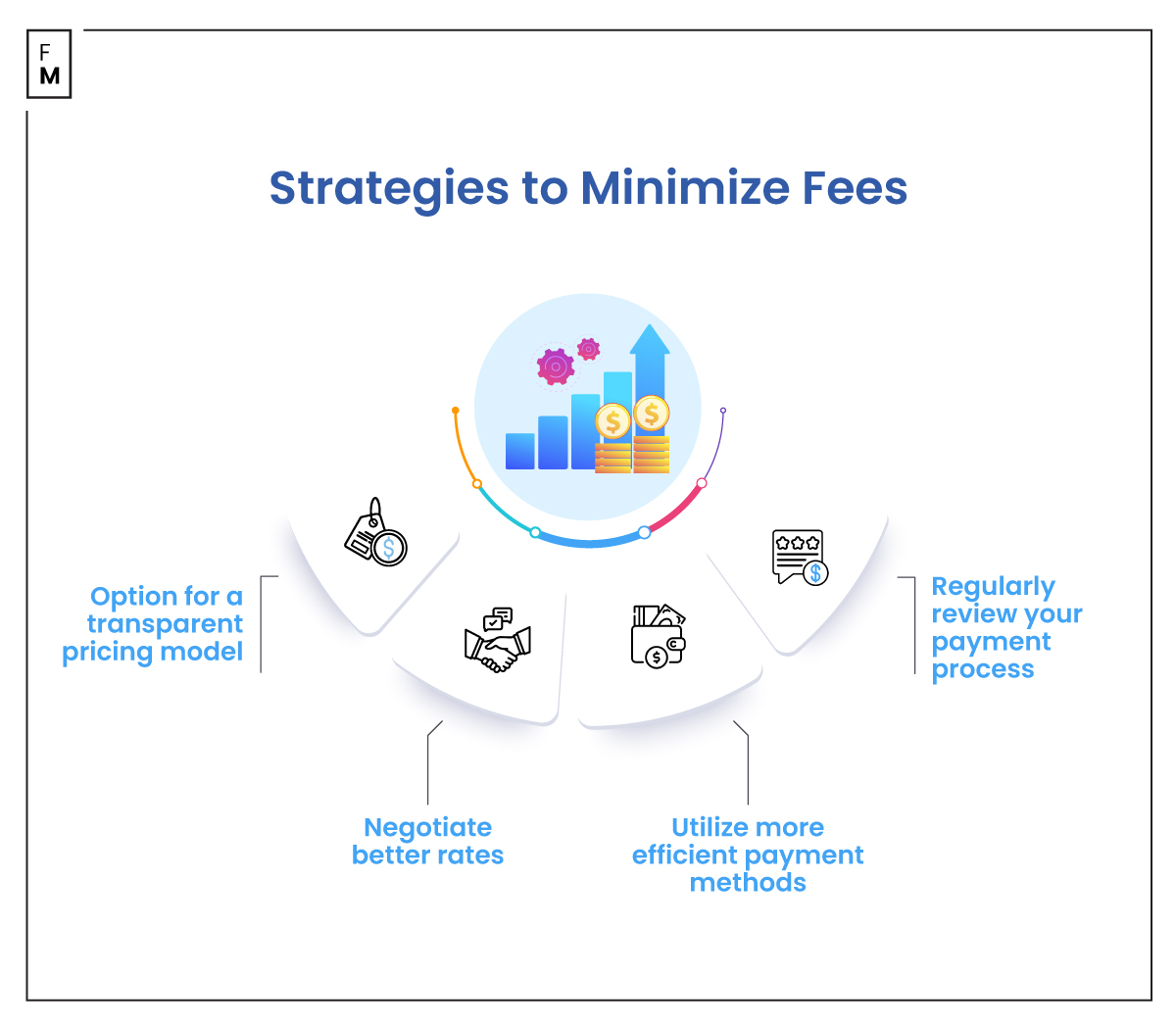
Strategies to Minimize Fees
Considering all these expenses, payment fees can substantially affect an establishment's profit margins and operational costs. Businesses, especially those in their growth phase, must strategize effectively to minimize these costs and protect their bottom line.
Here are a few practical strategies supported by my expertise to help businesses reduce their payment processing costs:
- Opt for a transparent pricing model: One of the first steps in effectively managing payment fees is choosing a payment processor that offers a transparent pricing model. Hidden charges can quickly accumulate, making it difficult for businesses to identify these costs, project, or accurately manage them.
- Negotiate better rates: Do not shy away from negotiating the rates with your payment processor. Many processors are willing to adjust their rates based on your transaction volumes or your business’s unique needs.
- Utilize more efficient payment methods: Certain payment methods come with higher processing fees. For example, transactions made using international credit cards or corporate cards might incur additional costs due to the higher risk or reward programs associated with these cards. By encouraging alternative payment methods or integrating more cost-effective solutions, businesses can reduce their overall fees.
- Regularly review your payment process: Analyzing your payment processing setup can uncover inefficiencies or opportunities for cost savings. These reviews can include identifying seldom-used services that are incurring fees or pinpointing areas where updating technology could lower overall payment processing rates.
Implement Advanced Fraud Detection Tools
Chargebacks due to fraud can result in significant fees and penalties. By implementing advanced fraud detection and prevention tools, businesses can reduce the risk of chargebacks. Take action today. Don't confine these strategies to just reading. Implement them, see them come to life, and witness the tangible difference they make to your financial outlay.
Adopting these strategies will not only streamline your operations but also markedly improve your bottom line. It's about harnessing control, enabling your growth, and, above all, fortifying your financial resilience in an ever-evolving business landscape.
Tackle the Unavoidable Costs and Remain Competitive
Fees are an unavoidable aspect of payment processing. However, by adopting strategic measures, you can significantly lower these costs, turning a potential hindrance into an opportunity for growth and greater efficiency.
Approach the strategies to minimize fees as part of a continual optimization process rather than a one-time effort. The cumulative effect of implementing these measures can be both substantial and rewarding, ensuring that your business remains competitive and financially robust.