For the past few years, cryptocurrencies have been widely discussed among investors and on a governmental level. This is hardly surprising - the price of Bitcoin and Ethereum has been rising ever since its creation, which means rising demand and an expanding market. 10 years ago the very idea was considered quite risky, but now in countries around the globe governments are thinking about how to legalize cryptocurrencies, and even create national ones.
The London Summit 2017 is coming, get involved!
We’ve decided to discuss the current state and the future of cryptocurrencies with the founder of UpTrader (brokerage software provider) Stanislav Vaneev, whose company currently works on several projects in China, the region were cryptocurrencies are in high demand. Stanislav is also the CEO of Grand Capital, a brokerage that accepts cryptocurrencies and is planning to implement them as a trading asset.
In the 9 years since Bitcoin was created, it has gone from $0.003 per 1000 BTC to $2700 per 1 BTC. What are the grounds for such a strong dynamic? Is there a limit to its growth? Will it bounce back at some point?
Let’s begin with the fact that Bitcoin initially was created as an alternative to the regulated currencies and it quite naturally found its use in certain niches.
For example, let’s look at the big and wealthy China, the country of huge amounts of money, developing businesses and, at the same time, strong government control over financial transactions. How is the shadow economy supposed to survive? How to avoid paying taxes? In China, cryptocurrencies are successfully used for this kind of purposes.
As a matter of fact, we develop Bitcoin integration solutions for Chinese Forex brokers. Now there are around 3 000 brokers in China that provide Forex and Binary Options trading services. Nevertheless, Forex is not completely legal in China and for that reason many brokers may take an interest in Bitcoin transactions.
As per the Bitcoin rate surge, there is an opinion that Bitcoin develops following the pyramid pattern, which means that it will continue rising as long as it is convenient for everyone, but sooner or later it will start bouncing back, as the currency is not backed by anything. As a result, the investors will turn to other cryptocurrencies, for example, Ethereum.
Ethereum is also gaining popularity. Will it be able to catch up with Bitcoin?
Judging by the dynamics, it can happen in the near future. Ethereum is 7 years younger than Bitcoin — it only appeared in 2015, but for the past several months it has jumped to the second place among other cryptocurrencies in terms of trading volumes. To a large extent, it has to do with the fact that the Ethereum has considered and corrected the main drawbacks Bitcoin is criticized for. For instance, Ethereum offers shorter transaction times.
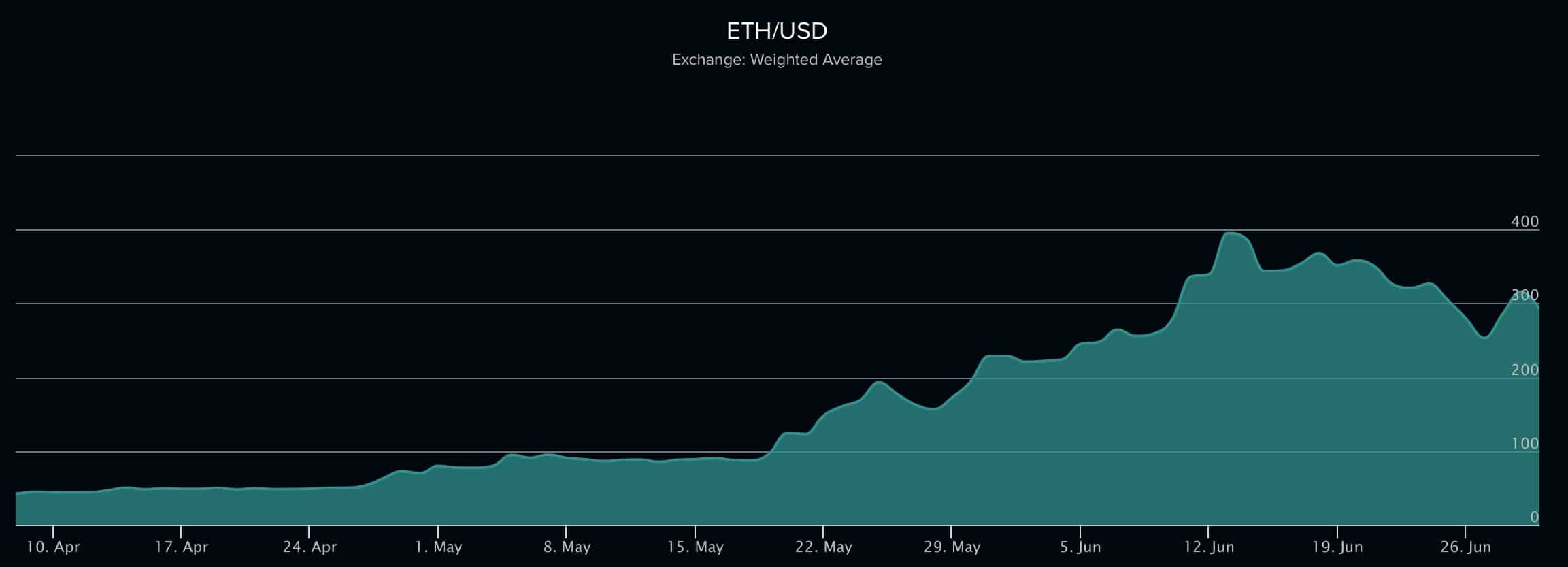
Ethereumprice.org
From the very beginning, Ethereum was wired to be mined on personal computers, unlike Bitcoin, which is mostly mined using special equipment, located at huge farms in China. That makes Ethereum much more attractive for ordinary users, which allows for the network to remain well distributed and more secure.
Do you think that the future of cryptocurrencies lies in centralization and integration into national currency systems?
In many respects, it is the right way. It will reduce the transaction times, the currency will start being backed by the government, it will lower the volatility levels and eliminate anonymity, which seems like a right decision in respect to the anti-terrorism measures.
However, it will allow creating a regulated Blockchain and won’t allow an opportunity to falsify transactions. The system will work faster and the commission on transactions will drop. Now the transaction cost ($2,7) is based on large expenses on computing resources that create unique signatures. But if all signatures are to be signed only by the Central Bank, the process will become much simpler and cheaper.
What other advantages do you see there, apart from counter-terrorism?
For example, the low transaction cost will allow micropayments, 1-cent Payments even. In theory, it may change the face of the Internet, as the websites will have a new type of clients. The clients will be visitors, not advertisers. Meaning that the websites will be able to receive profit from page views, instead of advertising. This will lead to a change in the advertisement market and content.
Stock exchanges refuse to accept Bitcoin. Why?
For the main part, the reason is the high volatility. The stock exchanges are afraid of losing their reputation. By allowing Bitcoin trading, they would acknowledge it as a real trading instrument. And in case of a steep fall, those investors who would have lost their funds will trust the exchange less. This is the reason why the exchanges are hesitant to go for it: “Bitcoin is an unproven instrument, we can not vouch for it.”
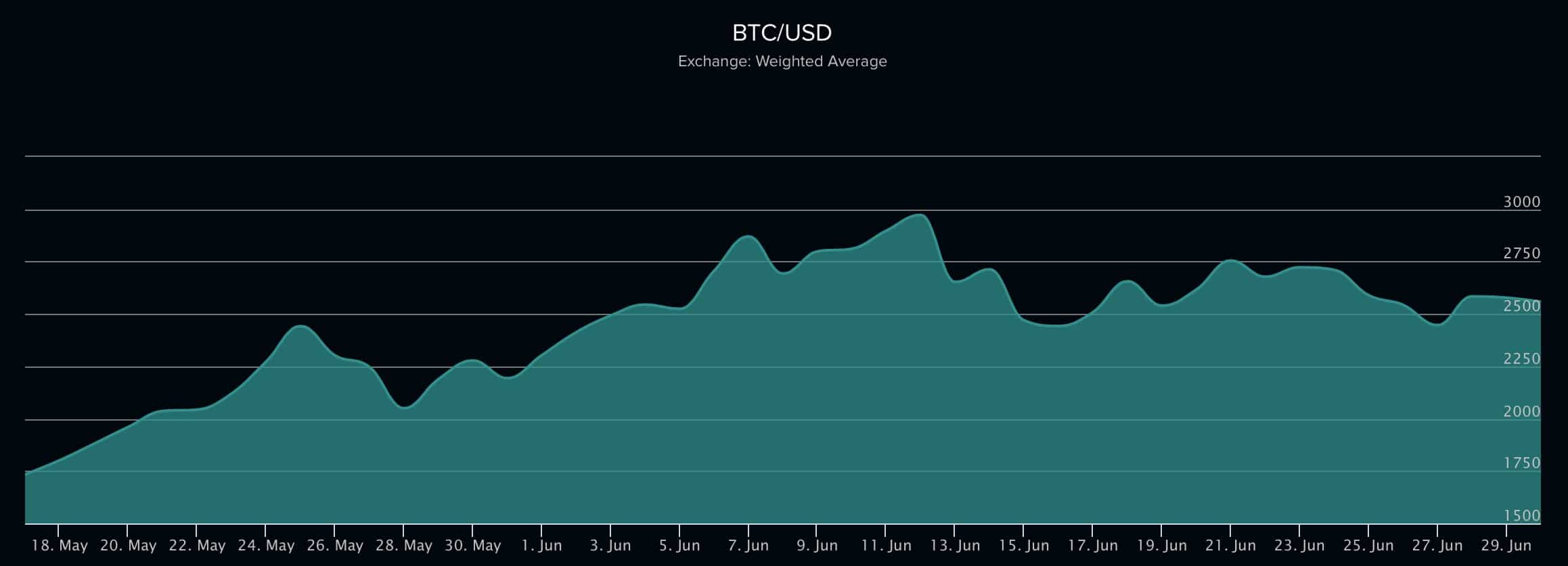
Ethereumprice.org
What risks does Bitcoin face, both currently and in the future?
If we speak of the evident risks, at the moment Bitcoin has internal and external ones. For the past several months, the transaction queue has grown 5 times and the transaction costs are often higher than those offered by the traditional systems, VISA and PayPal. Apparently, this problem can only be solved by a radical modernisation of blockchain technology, which requires consensus of the larger part of the market, which is yet to be reached.
What is the reason for the rising transaction times?
The problem is the blockchain technology. In order to carry out transactions, a 1-mb block is generated continuously, containing four thousand transactions. But as the Bitcoin network is growing, there are more and more transactions to be processed, which means that those transactions that don’t fit in the first block start to form a queue.
Are you planning to launch Bitcoin trading?
We tried launching cryptocurrency trading in 2014, but at that time it wasn’t so popular and our offering met a very little demand. Now we are planning to launch trading of practically all cryptocurrencies.
















