This article was submitted by ICM.com.
The latest economic data proves that the United States economy is among the best-performing economies in the world. During the second quarter of 2018, the US economy grew at its fastest rate in four years whereas the global economy has been showing signs of slowdown.
Meanwhile, the consumer confidence hit an eighteen-year high, supported by strong employment and higher wages. The Institute of Supply Management (ISM) survey data confirmed the healthy activity and solid momentum of both the manufacturing and services sectors.
However, critics are stating that further interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve could negatively affect this growth.
The Role of the Federal Reserve Bank
The Federal Reserve Bank is the entity in the United States responsible for implementing the monetary policy that promotes maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates.
The Federal Reserve can use several tools to ensure the implementation and enhancement of the targeted monetary policy. The main tools that the Federal Reserve can use are the open market operations, the discount rate, and the required reserve ratio.
Recent History of the Federal Reserve’s Actions:
Following the financial crash in 2008, the Federal Reserve had an ultra-loose monetary policy as interest rates were near the zero level and several asset purchase programs (quantitative easing 1, 2 &3) were introduced. The bank increased money supply in the American economy by injecting $4.5 trillion over five years to stimulate the economy.
As the overall economic performance improved, the Federal Reserve started tapering its asset purchases programs until it ended in October 2014.
On December 16, 2015, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) voted to raise the fed funds rate for the first time since the financial crisis, affirming that the Fed officials were satisfied with the economic progress. Meanwhile, they continued to closely monitor the three main economic indicators: Inflation, Growth, and Unemployment.
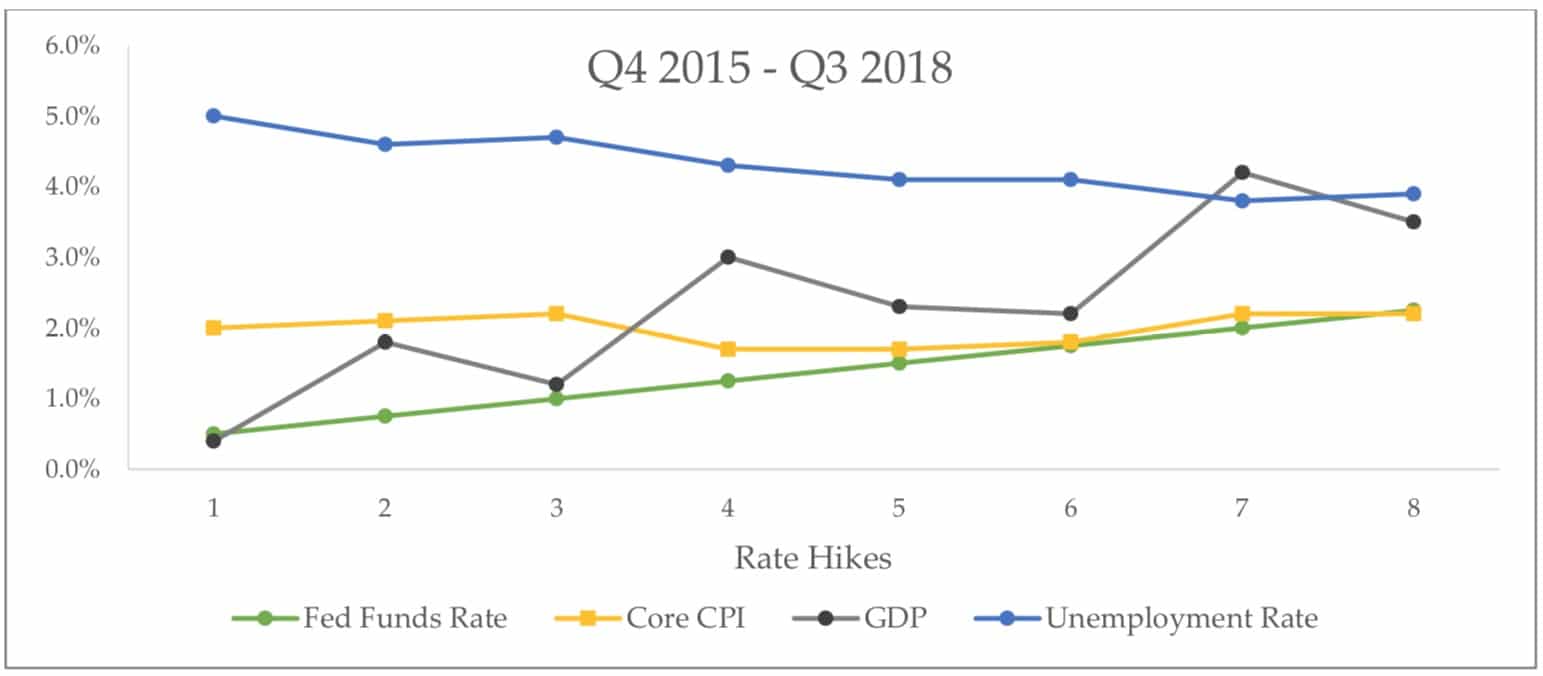
Data Source: Bloomberg
The Federal Reserve continued to raise interest rates as the overall macroeconomic indicators improved where the Unemployment Rate tumbled to 3.7% (lowest since 1969), the Core CPI steadied near the 2% level, and the GDP figures reflected healthy economic activity.
Fed officials are regularly announcing that interest rates will continue to rise until they reach neutral rate levels.
On the other hand, the latest Fed dot plot shows that the median projection for Fed Funds rate will settle between 2.25-2.50% in 2018, 3.00-3.25% in 2019, and steady at 3.25-3.50% in 2020/21.
The CME Fed Watch tool shows a high chance of a rate hike in December or January to 2.25- 2.50%, less than 50% chance of a rate hike in March, May, June, and July to 2.50-2.75%, and less than 35% chance of a rate hike in September and October to 2.75%-3.00%.
The Effects of Interest Rate Hikes
The main reason the Federal Reserve raises interest rates is to control inflation which is considered a threat to the economic performance on the long term. However, interest rate hikes would also affect the performance of the economy and its ability to grow.
Consequently, this makes it more difficult for the Federal Reserve to take decisions while maintaining stable growth rates and lower unemployment rate, and keeping inflation within the targeted rate.
Being a key element of the financial system, interest rate changes have a direct and critical effect on the financial markets. Usually, hiking interest rates drives the borrowing costs higher which is anticipated as a negative factor for the stock market by investors as higher rates will affect the performance of the companies and lead to lower valuations.
Meanwhile, traders will shift to the bond market that typically carries lower risk as the yields edge higher. This can lead to a plunge in the stock market. Also, the foreign Exchange markets will be affected as investors would seek opportunities in order to benefit from interest rate differentials.
In example, the interest rate hikes that were applied by the Federal Reserve throughout this year, provided a robust ground for the greenback to rise against a basket of other currencies that hold lower interest rates.
Neutral Interest Rates
As mentioned earlier, Fed officials have been constantly indicating that the interest rates will continue to rise until they reach their neutral level. What is meant by neutral interest rate level? Economists use several economic models to deduce where interest rates will be neutral.
The neutral rate of interest, is the interest rate where the economy maintains real GDP growth, maximum employment, and stable inflation. Currently, the United States economy is showing signs of steady growth, stable inflation (near 2% level), and maximum employment (unemployment rate at 3.7%).
How far is the Fed from reaching neutral interest rates? Are we there yet? Shall we expect three more hikes through 2019?
To obtain a more accurate assumption on the Fed’s next rate move, we should closely track the next wave of macroeconomic figures, with focus on growth, inflation, and unemployment.
Currently, the three are signaling that the fed is heading towards more rates hikes, despite the criticism of the United States president Donald Trump to the latest fed actions. Trump never missed an opportunity to attack the Fed’s interest rate path due to its effect on the US stock market.
Maybe, the Fed will eventually consider president Trump’s comments to prevent a stock market crash, especially after the sell-off that occurred during the past few weeks.












